A) A true difference in attitudes
B) A true difference in personality between John and Bob
C) A difference due to temporary personal factors
D) A difference due to situational factors
E) A difference due to variations in administration.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE?
A) The recording of a respondent's social class using the categories upper, middle, and lower represents the use of a nominal scale.
B) An ordinal scale can be transformed in any manner possible, provided that the basic ordering of the objects is maintained.
C) When the scale has an arbitrary zero point, it makes sense to say that A is twice as much as B.
D) Interval scales possess an absolute zero point whereas ordinal scales do not.
E) All of the above are all false.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first step in developing a measure of marketing constructs is to
A) generate sample items.
B) purify the measure.
C) assess validity.
D) specify the domain of the construct.
E) collect data.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ordinal scale represents a higher level of measurement than the nominal scale in that
A) the assigned numerals serve to identify the objects.
B) the magnitude of the differences in the objects is shown.
C) the assigned numerals represent the order as well as identifying the object.
D) it has a natural zero.
E) it has an arbitrary zero.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a scale to have ordinal properties, which of the following must be established?
A) If "a" is greater than "b," then "b" is not greater than "a."
B) If "a" is greater than "b" and "b" is greater than "c," then "a" is greater than "c."
C) If "a" is equal to "b" and "b" is equal to "c," then "a" is equal to "c."
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of scale is the following? Indicate your overall opinion about Dell computers by circling one of the following categories:

A) Stapel scale
B) Likert scale
C) Temperature scale
D) Graphic-rating scale
E) Itemized rating scale
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The zero scale value found when measuring marketing variables typically represents
A) the ordinal nature of the variable.
B) an absolute lack of an attribute.
C) the logical existence of a natural zero point.
D) a point of absolute zero magnitude.
E) a point of indifference to which the value zero is arbitrarily attached.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which attitude rating scale offers respondents the greatest degree of freedom in providing answers?
A) Itemized-ratings scale
B) Semantic-differential scale
C) Graphic-ratings scale
D) Summated-ratings (Likert) scale
E) Comparative-ratings scale
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
With an interval scale, the researcher can determine mean scores on measures in addition to median and modal scales.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If s/he wanted to use the highest level of measurement possible, the researcher measuring respondent age would most likely suggest using______________and a(n) ______________scale.
A) an open-ended item; interval
B) an open-ended item; ratio
C) age range categories; ordinal
D) age range categories; interval
E) an open-ended item; nominal
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following about ordinal data is TRUE?
A) An ordinal scale implies order but not identity.
B) The attribute being measured must possess the ordinal property to allow ordinal scaling that is meaningful.
C) With an ordinal scale we can say the difference between the first and second is the same as the difference between the second and the third.
D) The calculation of means is appropriate with ordinal data.
E) Grade point average is a good example of an ordinal scale.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With an interval scale
A) we cannot compare the absolute magnitude of numbers.
B) we cannot state that the difference between 0.25 and 0.50 is the same as the difference between 37.75 and 38.00.
C) there is a naturally-occurring zero point.
D) the median and the mode are the only permissible measures of average.
E) All of the above are all false concerning an interval scale.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One hundred sports writers are given a survey and asked to rank basketball players on categories such as rebounding, points scored, and assists. The results of the survey indicate that most sports writers agree on the top ten players, within the given categories. This is evidence of
A) reliability.
B) validity.
C) random error.
D) response error.
E) systematic error.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of "outs" in a baseball game is measured on a(n)
A) ratio scale.
B) interval scale.
C) ordinal scale.
D) nominal scale.
E) lambda scale.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
You should use the lowest level of measurement possible when developing a measure for some attribute.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of scale is the following? Indicate your opinion about services Delta Airlines provides, by placing an "X" at the appropriate position on the lines to the right of the services below.
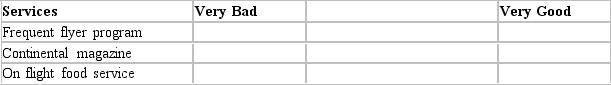
A) Stapel scale
B) Likert scale
C) Temperature scale
D) Graphic-rating scale
E) Itemized rating scale
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When using the ordinal scale, the number scale chose reflects the______________of the different options for that particular individual.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A research effort requires the researcher to use numbers to identify or categorize particular objects. The type of scale the researcher will use is
A) ratio.
B) ordinal.
C) interval.
D) nominal.
E) Conscious.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Reliability is necessary, but not sufficient, for establishing the validity of a measure.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The key features of the______________scale are a set of statements with which respondents indicate a level of agreement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 82
Related Exams