A) first or second degree
B) second or third degree
C) epidermal or dermal
D) thin or deep
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This stratum contains many layers of dead squamous cells.
A) Stratum basale
B) Stratum spinosum
C) Stratum granulosum
D) Stratum lucidum
E) Stratum corneum
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Indicate the statements that correctly describe partial thickness burns. (Check all that apply.)
A) They are subdivided into first- and second-degree burns.
B) They may involve only the epidermis.
C) They are also called third degree burns.
D) They involve the complete destruction of the epidermis and dermis.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Excessive shedding of this layer of the epidermis of the scalp is responsible for dandruff.
A) Stratum basale
B) Stratum spinosum
C) Stratum granulosum
D) Stratum lucidum
E) Stratum corneum
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adipose tissue in the subcutaneous layer
A) serves as a storage site for lipids, which can be used for energy.
B) helps to lower body temperature.
C) provides protection against infection.
D) is absent in infants.
E) connects the dermis with the epidermis.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dermis
A) contains no blood vessels.
B) functions as padding and insulation.
C) is divided into three distinct layers.
D) is responsible for most of the skin's structural strength.
E) does not contain connective tissue.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Melanin is found in which cells?
A) Only melanocytes
B) Both melanocytes and keratinocytes
C) Only keratinocytes
D) Both melanocytes and Langerhans cells
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Impetigo is caused by the bacterium ________.
A) Propionibacterium
B) Staphylococcus
C) Streptococcus
D) Herpes
E) Luteus
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By covering the whole body surface, the skin acts as a protective barrier and plays a role in ________.
A) excretion
B) immunity
C) circulation
D) respiration
E) digestion
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A skin cell in the stratum granulosum has experienced a mutation that altered its ability to produce keratin. Should this be a health concern for the individual?
A) No, because cells of the stratum granulosum are dying cells that do not reproduce, so the mutation will be isolated to the one cell.
B) Yes, because cells of the stratum granulosum divide by mitosis to produce keratin to protect the skin.
C) No, cells of the stratum granulosum only produce the waterproofing material in the skin.
D) Yes, without normal cell function in the stratum granulosum, the skin will lose color due to lack of melanin production.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The length of hair is determined by the
A) size of the hair bulb.
B) angle of the hair root.
C) rate of hair growth.
D) length of the resting stage.
E) age of the person.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Name the layer from which fingernails and toenails are derived.
A) Dermis
B) Epidermis
C) Subcutaneous tissue
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nail cells are produced by the ________.
A) lunula
B) cuticle
C) nail body
D) nail matrix
E) nail groove
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
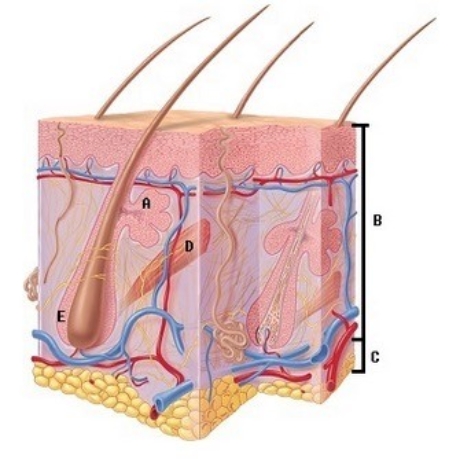 -What does structure "E" represent on the diagram?
-What does structure "E" represent on the diagram?
A) Hair follicle
B) Arrector pili
C) Epidermis and dermis
D) Subcutaneous tissue
E) Sebaceous gland
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A yellow pigment derived from plants that can impart a yellow color to the skin is ________.
A) melanin
B) keratin
C) collagen
D) carotene
E) elastin
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
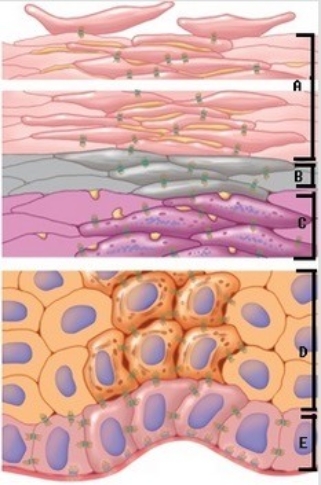 -The figure illustrates the layers of the epidermis. Which layer of the epidermis is "C"?
-The figure illustrates the layers of the epidermis. Which layer of the epidermis is "C"?
A) Stratum spinosum
B) Stratum corneum
C) Stratum basale
D) Stratum lucidum
E) Stratum granulosum
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proximal portion of the nail is the ________.
A) nail root
B) nail body
C) nail fold
D) eponychium
E) hyponychium
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One type of experimental contraceptive device is a skin patch that contains a chemical absorbed through the skin. Which of the following substances might be the type of chemical involved?
A) Proteins
B) Water-soluble substances
C) Lipid-soluble substances
D) Carbohydrates
E) Amino acids
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
On coming inside from the cold, students notice that their cheeks are red. This results from
A) constriction of the blood vessels in the epidermis of the cheeks.
B) dilation of the blood vessels in the dermis of the cheeks.
C) damage to the epidermis by the cold.
D) constriction of the sweat glands in the cheeks.
E) increased permeability of superficial vessels.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intact skin provides protection because
A) it forms a physical barrier against the entry of microbes.
B) its secretions keep the skin slightly alkaline.
C) the skin contains components of the excretory system.
D) the skin enhances water loss from the body.
E) macrophages roam in the epidermis.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 175
Related Exams