A) an automatic fiscal policy.
B) a discretionary revenue policy.
C) an annual tax policy.
D) a discretionary fiscal policy.
E) induced tax policy.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we compare the United States to France, the U.S. tax wedge is--------------------the French tax wedge.
A) equal to
B) larger than
C) smaller in the labor market and larger in the goods market than
D) not comparable to
E) smaller than
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Induced taxes are defined as taxes
A) that are avoided with the use of legal tax shelters.
B) that vary with real GDP.
C) we are forced to pay for services from the government.
D) that rise in recessions and fall in expansions.
E) enacted by Congress that explicitly state the amount to be paid.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply-side effects show that a tax cut on labor income-------------------- employment and-------------------- potential GDP.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) increases; does not change
D) decreases; decreases
E) decreases; increases
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To eliminate an inflationary gap using fiscal policy, the government could
A) only decrease taxes.
B) increase taxes.
C) increase government expenditure on goods and services and simultaneously decrease taxes by an equal amount.
D) increase government expenditure on goods and services and simultaneously increase taxes by an equal amount.
E) decrease the quantity of money.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier are
A) identical in size.
B) different in size and the government expenditure multiplier is larger.
C) not comparable because the government expenditure multiplier applies to aggregate demand and the tax multiplier applies to aggregate supply.
D) different in size and the tax multiplier is larger.
E) not comparable because the government expenditure multiplier applies to aggregate supply and the tax multiplier applies to aggregate demand.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy has a structural deficit of $25 billion and a cyclical deficit of $75, we can conclude that the current budget deficit is -------------------- billion.
A) $50
B) $75
C) $0
D) $25
E) $100
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The national debt is the amount
A) by which government outlays exceed tax revenue in a given year.
B) of all future entitlement spending.
C) of debt outstanding that arises from past budget deficits.
D) by which government tax revenue exceed outlays in a given year.
E) of government outlays summed over time.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to reduce inflationary pressure on the economy, what fiscal policy can the government use?
A) cut interest rates
B) increase the quantity of money
C) raise taxes
D) increase government expenditure on goods and services
E) cut taxes
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cut in the income tax rate --------------------the tax wedge and employment, saving, and-------------------- investment.
A) does not change; increases
B) increases; increases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; does not change
E) increases; decreases
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If government expenditure increases by $200 billion and taxes simultaneously increase by $200 billion, then aggregate demand
A) decreases no matter what happens to aggregate supply.
B) remains the same.
C) increases no matter what happens to aggregate supply.
D) increases only if aggregate supply decreases.
E) increases only if aggregate supply increases.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a tax cut increases aggregate demand more than aggregate supply, real GDP-------------------- and the price level --------------------.
A) increases; falls
B) decreases; rises
C) increases; rises
D) decreases; falls
E) increases; does not change
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Needs-tested spending
A) is directing government spending and taxes to states that need the most help.
B) is giving tax cuts to wealthy people so they will increase their spending.
C) cannot be changed without changes in the laws.
D) includes homeland defense spending.
E) includes transfer payments such as food stamps and unemployment benefits.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
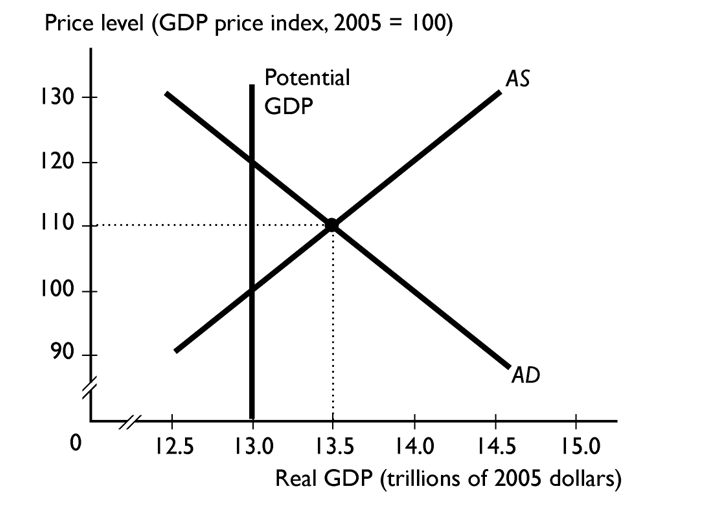 If an economy is at the short-run equilibrium illustrated by the figure above, a discretionary fiscal
Policy to adjust the economy to full employment is to
If an economy is at the short-run equilibrium illustrated by the figure above, a discretionary fiscal
Policy to adjust the economy to full employment is to
A) decrease taxes.
B) increase taxes and decrease government spending simultaneously.
C) increase government spending.
D) decrease the quantity of money.
E) increase the quantity of money.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The balanced budget multiplier is
A) positive because the magnitude of government expenditure multiplier is smaller than the magnitude of tax multiplier.
B) positive because the magnitude of government expenditure multiplier is larger than the magnitude of tax multiplier.
C) equal to zero.
D) negative because the magnitude of the tax multiplier is larger than the magnitude of the government expenditure multiplier.
E) negative because the magnitude of government expenditure multiplier is larger than the magnitude of the tax multiplier.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
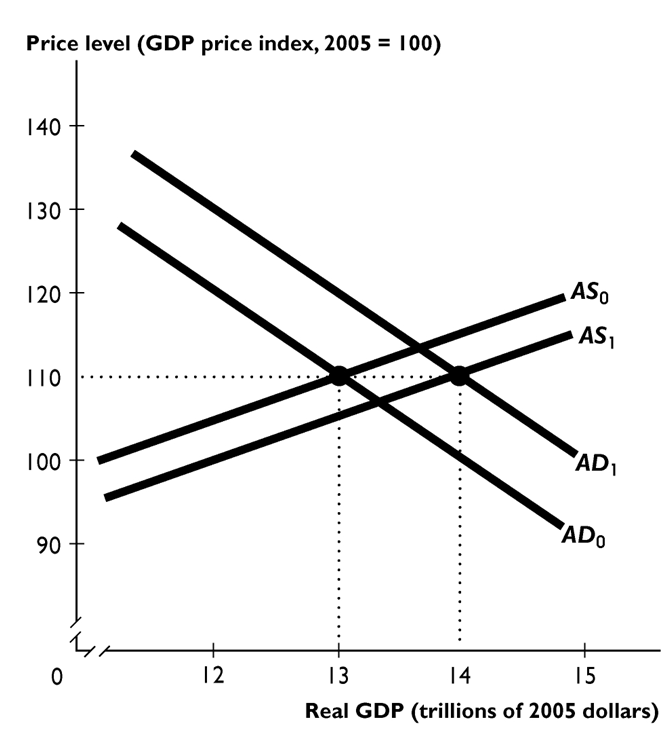 -
Suppose the shift from AD0 to AD1 and from AS0 to AS1 is the result of fiscal policy. If the effect on aggregate demand was larger than the figure above shows, as a result the price level would be--------------------
110 and real GDP would be --------------------$14 trillion.
-
Suppose the shift from AD0 to AD1 and from AS0 to AS1 is the result of fiscal policy. If the effect on aggregate demand was larger than the figure above shows, as a result the price level would be--------------------
110 and real GDP would be --------------------$14 trillion.
A) equal to; larger than
B) higher than; larger than
C) smaller than; less than
D) smaller than; larger than
E) equal to; equal to
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Needs-tested spending
A) decreases in recessions and increases in expansions.
B) increases in recessions and decreases in expansions.
C) does not change with the level of economic activity.
D) is always increasing regardless of whether we are in an expansion or a recession.
E) cannot be changed unless the government changes the spending laws.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Needs-tested spending is defined as
A) spending by the President on the White House.
B) spending that increases in expansions and decreases in recessions.
C) spending by Congress on its own perks of office.
D) spending on programs for people qualified to receive benefits.
E) taxes paid by those qualified by their income.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the United States for the year 2012, the federal government had a-------------------- so the national debt was-------------------- .
A) budget surplus; decreasing
B) budget deficit; decreasing
C) budget surplus; increasing
D) budget deficit; increasing
E) balanced budget; not changing
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mainstream economists believe that Keynesian economists overstate the effect of the multiplier effect. Which of the following statements would mainstream economists NOT consider to be accurate?
A) A fiscals stimulus does not provide a 'free lunch' but does 'crowd out' private consumption expenditure and investment.
B) A fiscal stimulus is a vital tool to fight recession and depression due to the multiplier effect.
C) Effects of a fiscal stimulus are incapable of working fast enough to make a difference.
D) A fiscal stimulus results in bigger government, lower potential GDP, and slower real GDP growth.
E) Effects of a fiscal stimulus are small and short lived.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 133
Related Exams