A) Mitotic spindle
B) Centrioles
C) Kinetochore
D) Microtubules
E) Centromere
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves contraction of a ring of ____ microfilaments.
A) tubulin plus actin
B) actin plus myosin
C) cyclin plus myosin
D) cohesin plus actin
E) cyclin plus actin
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the stage of meiosis with its corresponding event(s).
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-1
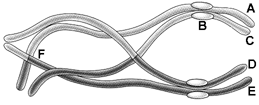
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two homologous chromosomes?
In the accompanying figure, which combination of letters accurately represents two homologous chromosomes?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) B and F
E) D and E
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mitotic spindle is made of
A) motor proteins.
B) condensin.
C) histones.
D) Z rings.
E) microtubules.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is produced by meiosis?
A) Somatic cells
B) Animal gametes
C) Polyploid cells
D) Diploid cells
E) Zygotes
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the stage of meiosis with its corresponding event(s).
Correct Answer
True/False
Bacteria divide asexually by mitosis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the stage of mitosis with its corresponding event(s).
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
During prophase I, each chiasma represents
A) the remnants of the nuclear envelope.
B) the remnant of the nucleolus.
C) a newly formed haploid gamete.
D) a site of crossing-over.
E) the site where sister chromatids are connected.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Briefly describe the advantages of asexual reproduction of unicellular organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
The process produces genetically identic...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
In fungi and protists, gametes produced by ____ of haploid cells fuse to form a ____ zygote, which then undergoes ____ to restore the haploid chromosome number.
A) mitosis, diploid, meiosis
B) meiosis, diploid, mitosis
C) mitosis, haploid, meiosis
D) meiosis, haploid, mitosis
E) mitosis, diploid, mitosis
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During prophase, ____ is(are) compacted into visible chromosomes.
A) chromatin
B) centrioles
C) centromeres
D) kinetochores
E) tetrads
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Microtubules of the mitotic spindle attach directly to each chromosome at the centromere.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ____ is responsible for the separation of the chromosomes during the ____ of mitosis.
A) cell wall; anaphase
B) mitotic spindle; interphase
C) mitotic spindle; anaphase
D) kinetochore; prophase
E) centromere; telophase
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if meiosis did not occur in sexually reproducing organisms?
A) The growth of the zygote would be halted.
B) Mitosis would be sufficient to produce haploid gametes.
C) The gametes would remain haploid.
D) The chromosome number would double in each generation.
E) The eggs would be haploid, but the sperm would be diploid.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For each animal cell that begins oogenesis, the number of ova produced is four.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The M phase of the cell cycle involves two main processes:
A) mitosis and cytokinesis.
B) meiosis I and meiosis II.
C) homologous pairing and crossing over.
D) interphase and mitosis.
E) mitosis and meiosis.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 78 of 78
Related Exams