A) less of X and more of Y.
B) more of X and less of Y.
C) more of both X and Y.
D) less of both X and Y.
E) neither X nor Y.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We would expect the total utility of water to be high but its marginal utility to be low. Why?
A) Because water is a fluid and we don't need fluids to live as much as we need food.
B) Because we need water to live and there is so much of it.
C) Because we need water to live and there is very little of it.
D) Because water's price is low.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is the solution to the diamond-water paradox: Those things that have high value in use sometimes have low prices because they are consumed at low __________ utility; those things that have low value in use sometimes have high prices because they are consumed at high __________utility.
A) marginal; total
B) total; total
C) total; marginal
D) marginal; marginal
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the government provides peanut butter to everyone free of charge and everyone consumes it to the point at which he receives no additional satisfaction from another spoonful. According to economics, is this necessarily good?
A) Yes, because everyone is satisfied.
B) No, because there might be some cases where the resources used to produce peanut butter could have been better used to produce more of other products.
C) Yes, because the law of diminishing marginal utility indicates that in order to get the greatest amount of satisfaction from the use of resources, people should consume as much of every good as they can.
D) Yes, because of the law of supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 20-6
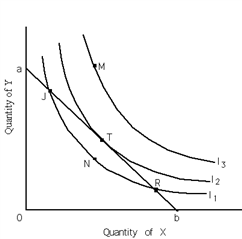 Refer to Exhibit 20-6. I1, I2 and I3 are indifference curves and line ab is the relevant budget constraint. The equilibrium position for the consumer is at
Refer to Exhibit 20-6. I1, I2 and I3 are indifference curves and line ab is the relevant budget constraint. The equilibrium position for the consumer is at
A) any point on the budget constraint.
B) point M.
C) point J.
D) point T.
E) point R.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the rate of increase of total utility declines as the quantity consumed of a good increases, it follows that marginal utility must be
A) declining.
B) rising.
C) staying constant.
D) negative.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following settings is an interpersonal utility comparison being made?
A) Brandon says, "I got a lot more satisfaction out of eating pizza than today than I did yesterday."
B) Stephanie says, "I don't know what Taylor is feeling or thinking; I can't read a person's heart or mind."
C) David says to Maria, "I know you like economics a lot more than I do."
D) Wendy says, "I got a lot less satisfaction from studying today than I did last week."
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Don receives 100 utils from consuming two oranges. The utility he derives from consuming the second orange equals 30 utils. The information provided
A) is consistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
B) is inconsistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) is sufficient to determine the quantity of oranges Don will consume.
D) lends support to the inferiority of oranges as consumer goods.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) An extra dollar earned by a millionaire necessarily brings him or her less utility than an extra dollar earned by a poor person.
B) If marginal utility is constant, then total utility for two units of a good is equal to the marginal utility of the second unit of the good.
C) The marginal and total utility of a good are the same for the first unit of the good.
D) Total utility will rise if marginal utility is negative.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dan is currently consuming 10 Cokes and 5 slices of pizza per week such that the marginal utility of the tenth Coke is 12 utils and that of the fifth slice of pizza is also 12 utils. How should Dan redirect his purchases so as to attain consumer equilibrium?
A) He should buy more pizza slices and less Coke.
B) He should buy fewer pizza slices and more Coke.
C) He is currently attaining consumer equilibrium and should not redirect his purchases.
D) He could gain more satisfaction by buying less of both and more of something else.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person is in consumer equilibrium, and then the price rises for one of the goods she purchases. If she wants to restore herself to consumer equilibrium, she will (most likely)
A) buy less of the good whose price has risen and more of the relatively lower priced goods.
B) try to increase the marginal utility she receives from the good whose price has risen.
C) try to decrease the marginal utility she receives from the goods whose prices did not rise.
D) buy more of both the good whose price has risen and of the goods whose prices have not risen.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person's income and the prices of both goods all rise by the same percentage, then her budget constraint
A) moves inward toward the origin, and its slope remains the same.
B) moves outward away from the origin, and its slope changes.
C) moves outward away from the origin, and its slope remains the same.
D) does not change in any way.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose Alice receives 150 utils from consuming one hamburger and 70 utils from consuming a second hamburger. What is the marginal utility of the second hamburger?
A) 220 utils
B) 150 utils
C) 70 utils
D) 0 utils
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 20-1 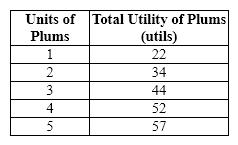 Refer to Exhibit 20-1. The marginal utility of the third plum is
Refer to Exhibit 20-1. The marginal utility of the third plum is
A) 17 utils.
B) 10 utils.
C) 8 utils.
D) 3 utils.
E) cannot be determined
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you are eating buffalo wings at a local happy hour. The total utils from doing so after the fourth, fifth, sixth, and seventh wings are 80, 116, 136, 150, respectively. The marginal utility of the sixth wing is __________ utils.
A) 14
B) 136
C) 20
D) 22.7
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A util is an artificial construct used as a means of measuring the
A) price of a good.
B) satisfaction one receives from the consumption of a good.
C) costs of producing a good.
D) difference between the price and the value of a good.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal utility of a good is negative, then
A) consumers should buy less of it.
B) consumers will consume it only if it is free.
C) consumers should buy more of it to make its marginal utility positive.
D) the law of diminishing marginal utility is being violated.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of consumer choice assumes that consumers attempt to maximize
A) the difference between total utility and marginal utility.
B) average utility.
C) total utility.
D) marginal utility.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 20-1 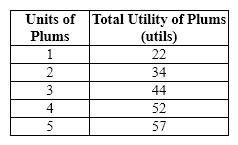 Refer to Exhibit 20-1. The marginal utility of the fourth plum is
Refer to Exhibit 20-1. The marginal utility of the fourth plum is
A) 8 utils.
B) 2 utils.
C) 10 utils.
D) 13.5 utils.
E) 50 utils.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 20-3 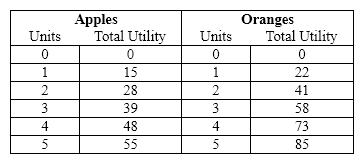 Refer to Exhibit 20-3. Assume that the price of oranges increases to $2, while the price of apples remains at $1, and Linda allocates $5 of the weekly food budget to purchasing apples and oranges. If Linda wants to maximize her utility, her new consumption bundle will consist of
Refer to Exhibit 20-3. Assume that the price of oranges increases to $2, while the price of apples remains at $1, and Linda allocates $5 of the weekly food budget to purchasing apples and oranges. If Linda wants to maximize her utility, her new consumption bundle will consist of
A) 1 apple and 2 oranges.
B) 3 apples and 1 orange.
C) 5 apples and no oranges.
D) 2 apples and 1 orange.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 179
Related Exams