A) millions of; 46
B) four; 23
C) one; 46
D) millions of; 23
E) four; 46
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The surgical removal of the foreskin is called
A) circumcision.
B) orchidectomy.
C) tubectomy.
D) vasectomy.
E) pupectomy.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pad of adipose tissue covering the pubic symphysis is the
A) hymen.
B) clitoris.
C) labia majora.
D) prepuce.
E) mons pubis.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pocket formed between the uterus and the posterior wall of the bladder is the
A) vestibule.
B) vesico-uterine pouch.
C) recto-uterine pouch.
D) broad ligament.
E) uterine hilum.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The organ that transports the ovum to the uterus is the
A) uterosacral ligament.
B) vagina.
C) uterine (Fallopian) tube.
D) infundibulum.
E) myometrium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The male gonad is called a(n)
A) seminal vesicle.
B) epididymis.
C) rete.
D) testis.
E) prostate.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The broad ligament attaches to all of the following organs except the
A) ovaries.
B) uterine tubes.
C) uterus.
D) oviducts.
E) urinary bladder.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The small paired structures at the base of the penis that secrete a thick, alkaline mucus are the
A) seminal vesicles.
B) prostate glands.
C) preputial glands.
D) Bartholin glands.
E) bulbo-urethral glands.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur after menopause?
A) Menstrual cycles cease.
B) Ovulation ceases.
C) Estrogen levels rise.
D) GnRH secretion increases.
E) FSH secretion increases.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ consists of the follicle cells that cling to the oocyte after ovulation.
A) stroma
B) corpus albicans
C) antrum
D) zona pellucida
E) corona radiata
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -At what stage of development is the oocyte during ovulation? (Figure 28-22)
A) primordial
B) oogonium
C) primary oocyte
D) secondary oocyte
E) ovum
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary follicle develops from the
A) ovarian hilum.
B) tunica albuginea.
C) primordial follicle.
D) ovarian stroma.
E) granulosa cells.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The expanded, initial segment of the uterine tube closest to the ovary is called the
A) vaginal fornix.
B) infundibulum.
C) tunnel.
D) ampulla.
E) os.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -Which erectile tissue is split into two cylindrical masses that surround a central artery? Which erectiletissue surrounds the urethra? (Figure 28-7)
A) corpus spongiosum; corpora cavernosa
B) corpora cavernosa; corpus spongiosum
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 28-2 The Female Reproductive System
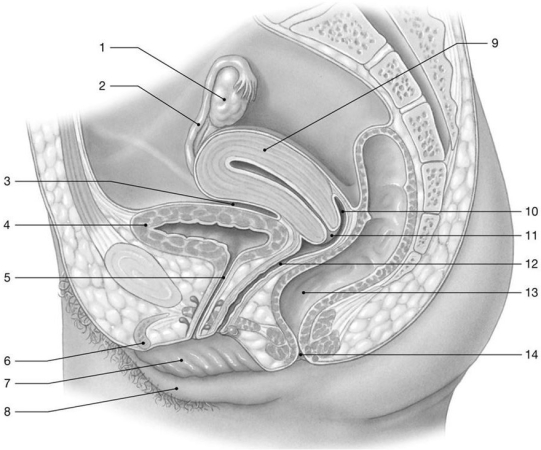 Use Figure 28-2 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "7."
Use Figure 28-2 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "7."
A) vagina
B) clitoris
C) greater vestibular gland
D) labium minus
E) labium majus
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When spermatogonia divide, the daughter cells are called
A) spermatogonia.
B) spermatocytes.
C) spermatids.
D) sperm.
E) Sertoli cells.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cells that are formed during spermatogenesis by meiosis I are called
A) spermatogonia.
B) primary spermatocytes.
C) secondary spermatocytes.
D) spermatids.
E) sperm.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are inguinal hernias generally associated with males?
A) Males have a gene on the Y chromosome that codes for inguinal hernia, whereas women do not have the Y chromosome.
B) Women have a thicker set of skeletal muscles in the abdominal wall compared to men.
C) Males work more strenuously than women, thereby damaging the abdominal wall.
D) Males have a canal through the abdominal wall that the testes move through, and it often does not close up properly.
E) The groin area is genetically weaker in men than in women because of the presence of the penis and testes.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -What is the name of the cell at each stage of sperm development, from mitosis to spermiogenesis? (Figure-289)
A) secondary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm, spermatogonium, primary spermatocyte
B) spermatids, spermatogonium, primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, sperm
C) primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, spermatogonium, spermatids, sperm
D) spermatogonium, primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, spermatids, sperm
E) spermatogonium, spermatids, primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, sperm
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding erection is false?
A) It involves parasympathetic stimulation.
B) Vascular channels in the erectile tissue become engorged with blood.
C) Dilation of penile arteries occurs.
D) It involves nitric oxide production by neurons.
E) It is commonly the result of plaque in the blood vessels of the penis.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 203
Related Exams