A) altering the diameter of the respiratory passageways
B) elevating hairs on the arm
C) forcing blood from the heart into the major arteries
D) moving food materials along the digestive tract
E) forcing urine out of the urinary tract
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skeletal muscle fibers are formed from embryonic cells called
A) sarcomeres.
B) myofibrils.
C) myoblasts.
D) fascicles.
E) myomeres.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The protein that is found in the Z line of a sarcomere is called ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following hormones directly stimulates growth of muscle tissue,leading to increased muscle mass?
A) epinephrine
B) thyroid hormone
C) testosterone
D) parathyroid hormone
E) calcitonin
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Put the following structures in order from superficial to deep: 1. muscle fiber 2) perimysium 3) myofibril 4) fascicle 5) endomysium 6) epimysium
A) 1,5,4,3,2,6
B) 6,2,5,4,1,3
C) 6,2,4,5,1,3
D) 1,3,5,6,4,2
E) 2,3,1,4,6,5
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since each myofibril is attached at either end of the muscle fiber,when sarcomeres shorten,the muscle fiber
A) lengthens.
B) shortens.
C) strengthens.
D) weakens.
E) pulls from the middle.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the recovery period following exercise,all of the following are true,except
A) lactic acid is removed from muscle cells.
B) the muscle actively produces ATP.
C) muscle fibers are unable to contract.
D) oxygen is consumed at above the resting rate.
E) heat is generated.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single motor neuron together with all the muscle fibers it innervates is called
A) an end foot.
B) an end plate.
C) a motor unit.
D) a dermatome.
E) a myotome.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At peak levels of muscle exertion the mitochondria can supply
A) all of the energy required by the muscle.
B) 80 percent of the energy required by the muscle.
C) more than half of the energy required by the muscle.
D) only about one-third of the energy required by the muscle.
E) only about 10 percent of the energy required by the muscle.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Describe the basic sequence of events that occurs as an action potential arrives at the neuromuscular junction and is transmitted to the muscle cell.
Correct Answer

verified
The action potential triggers the exocyt...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
The type of contraction in which the muscle fibers do not shorten is called
A) tetany.
B) treppe.
C) concentric.
D) isotonic.
E) isometric.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The repeating unit of a skeletal muscle fiber is the
A) sarcolemma.
B) sarcomere.
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) myofibril.
E) myofilament.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The thin filaments of striated muscle are made primarily of which protein(s) ?
A) actin
B) tropomyosin
C) troponin
D) nebulin
E) All of the answers are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a muscle is stimulated repeatedly at a high rate,the amount of tension gradually increases to a steady maximum tension.This is called
A) incomplete tetanus.
B) complete tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) wave summation.
E) recruitment.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each thin filament consists of
A) two actin protein strands coiled helically around each other.
B) chains of myosin molecules.
C) six molecules coiled into a helical structure.
D) a rod-shaped structure with "heads" projecting from each end.
E) a double strand of myosin molecules.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
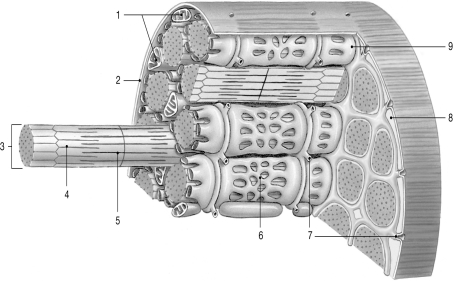 Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-What physiological process occurs in the structure labeled "7"?
Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-What physiological process occurs in the structure labeled "7"?
A) release of neurotransmitter
B) conduction of the action potential into the cell interior
C) activity of acetylcholinesterase
D) release of protein into the muscle fiber
E) the sliding filament theory
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The delicate connective tissue that surrounds the skeletal muscle fibers and ties adjacent muscle fibers together is the
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) epimysium.
D) superficial fascia.
E) periosteum.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-Where would calcium ions be predominately found?
Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-Where would calcium ions be predominately found?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 9
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following would the motor units have the fewest muscle fibers?
A) muscles of the neck
B) postural muscles of the back
C) muscles that control the eyes
D) thigh muscles
E) calf muscles
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-Identify the structure labeled "1."
Figure 10-1 Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Use Figure 10-1 to answer the following question:
-Identify the structure labeled "1."
A) mitochondria
B) glycogen
C) ATP
D) myofibril
E) synaptic vesicle
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 135
Related Exams