A) viscosity.
B) specific gravity.
C) packed volume.
D) hematocrit.
E) differential cell count.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sign of thrombocytopenia would be
A) a drop in oxygen-carrying capacity.
B) allergic reactions.
C) bacterial infections.
D) excessive clotting.
E) bleeding.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The level of erythropoietin in the blood would rise due to all of the following except
A) anemia.
B) high altitude.
C) as a consequence of hemorrhage.
D) periods of fasting.
E) when blood flow to the kidneys is disrupted.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
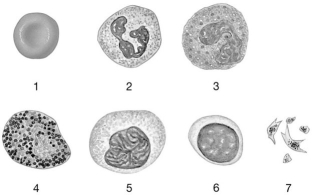 Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed Elements
Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the cell labeled "2."
Figure 19-1 The Origins and Differentiation of Formed Elements
Use Figure 19-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the cell labeled "2."
A) lymphocyte
B) eosinophil
C) basophil
D) neutrophil
E) monocyte
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pernicious anemia caused by a lack of intrinsic factor is specifically treated by
A) oral doses of iron.
B) injections of iron.
C) oral doses of vitamin B₁₂.
D) injections of vitamin B₁₂.
E) blood transfusion.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Soon after donating 0.5 liters of blood,one would expect
A) an increased reticulocyte count.
B) an increased platelet count.
C) an increased erythrocyte count.
D) an increased neutrophil count.
E) increased levels of clotting factors.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are common sources of vitamin K?
A) green vegetables
B) organ meats
C) whole grains
D) intestinal bacteria
E) All of answers are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average life span of a red blood cell is
A) 24 hours.
B) 1 month.
C) 4 months.
D) about 1 year.
E) many years.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plasma thromboplastin is a factor in the ________ pathway.
A) extrinsic
B) intrinsic
C) common
D) retraction
E) fibrinolytic
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In adults,the only site of red blood cell production,and the primary site of white blood cell formation,is the
A) liver.
B) spleen.
C) thymus.
D) red bone marrow.
E) yellow bone marrow.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Thyroid-binding globulin is an example of which kind of plasma protein?
A) metalloprotein
B) steroid-binding
C) hormone-binding
D) apolipoprotein
E) transport albumin
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When checking the efficiency of gas exchange,it may be necessary to draw a blood sample from
A) the heart.
B) the lungs.
C) an artery.
D) a vein.
E) capillaries.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is reduced,owing to a low blood hemoglobin concentration,is called
A) thrombocytopenia.
B) leukopenia.
C) polycythemia.
D) anemia.
E) leukocytosis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A substance that activates plasminogen might be useful to
A) cause clots to form faster.
B) cause clot dissolution to proceed faster.
C) initiate clot formation.
D) mimic heparin.
E) recruit neutrophils to an infection.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Areas in a vessel wall where large quantities of lipid accumulate are called
A) thrombi.
B) emboli.
C) plaques.
D) clots.
E) occlusions.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is responsible for the RBC's ability to transport oxygen and CO₂.
A) Hemoglobin
B) Fibrinogen
C) Albumin
D) Transferrin
E) Ferritin
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The intrinsic pathway of coagulation is activated by the
A) sticking of platelets to each other.
B) activation of Factor XII by platelet factors.
C) release of tissue factor (Factor III) by damaged endothelium.
D) release of heparin from the liver.
E) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
White blood cells that are increased in allergic individuals are the
A) neutrophils.
B) eosinophils.
C) platelets.
D) lymphocytes.
E) monocytes.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 158 of 158
Related Exams