A) mycorrhizal fungi
B) chytrids
C) lycophytes
D) yeasts
E) lichens
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While walking in the woods, you come across some low-growing plants clustered at the base of a tree. You collect one as a specimen for biology class. Upon examination in the lab, you find that the leaf-, stem-, and root-like structures contain no vascular tissue. The plant is
A) a lycophyte.
B) an angiosperm.
C) a gymnosperm.
D) a bryophyte.
E) not a plant but a charophyte.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By definition, a fruit is derived from the
A) archegonium.
B) corolla.
C) calyx.
D) ovary.
E) stamen.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these has a diploid stage in their life cycle?
A) mosses only
B) mosses and ferns but not gymnosperms or angiosperms
C) gymnosperms and angiosperms but not mosses or ferns
D) mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms
E) angiosperms only
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these would be best able to reproduce during a period with only light rainfall?
A) lycophytes
B) gymnosperms
C) bryophytes
D) ferns
E) No plants can reproduce except during rainy weather.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Endosperm is a _____ tissue.
A) haploid (n)
B) vascular
C) diploid (2n)
D) cotyledon
E) triploid (3n)
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In black bread mold, spores are produced in
A) clublike structures of the gills.
B) sporangia.
C) carpels.
D) sori.
E) mycorrhizae.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would you predict as a likely consequence of eradicating all fungi from soil before sowing it with plant seeds?
A) Although the plants might grow, they would be unlikely to thrive due to the lack of mycorrhizal fungi.
B) The plants would grow much more vigorously because they would not have to compete with fungi for nutrients.
C) The plants would grow much more vigorously because they would not need to fight off fungal diseases.
D) No plants would be able to grow, because mycorrhizal fungi are essential for the germination of seeds.
E) The plants would grow as normal, because the presence or absence of fungi has no impact on plants.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is mismatched?
A) mushroom-fruiting body
B) angiosperm-flower
C) lycophyte-microphyll
D) charophyte-hypha
E) gymnosperm-seed
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 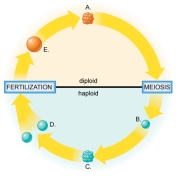 -Which part of the figure represents the gametophyte?
-Which part of the figure represents the gametophyte?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fermentation capabilities of _____ are used to produce bread and alcoholic beverages.
A) yeasts
B) chytrids
C) lichens
D) mycorrhizal fungi
E) molds
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about fungi is incorrect?
A) Fungi are chemoheterotrophic by absorption.
B) Fungi are generally motile.
C) Adult fungal cells are haploid.
D) Fungal cell walls are composed of chitin.
E) Fungi are thought to be descendants of a flagellated protist.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most fungi in the environment function as
A) parasites.
B) saprotrophs.
C) photoautotrophs.
D) producers.
E) predators.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a fungal life cycle, which of the following is/are diploid?
A) the zygote only
B) the spores only
C) the hyphae only
D) the hyphae and spores but not the zygote
E) the zygote, spores, and hyphae
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gametophyte is the dominant generation in
A) angiosperms.
B) gymnosperms.
C) ferns.
D) mosses.
E) all land plants.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following provide protection and nourishment to the embryo?
A) all plants
B) angiosperms only
C) gymnosperms only
D) bryophytes only
E) lycophytes only
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is not a fungal disease (mycosis) ?
A) wheat rust
B) ringworm
C) athlete's foot
D) oral thrush
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which feature is believed to have been the first step in the evolution of land plants from the green algae?
A) protection of the embryo
B) evolution of vascular tissue
C) evolution of microphylls
D) evolution of seeds
E) evolution of flowers in order to attract pollinators
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these does not belong to the angiosperm life cycle?
A) double fertilization
B) pollen
C) megaspore
D) flagellated sperm
E) microspore
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Apples, oranges, peanuts, and rice grains are produced by
A) gymnosperms.
B) bryophytes.
C) angiosperms.
D) charophytes.
E) lycophytes.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 56
Related Exams