A) 1.6 × 10-2 mol L-1
B) 3.1 × 10-2 mol L-1
C) 6.2 × 10-2 mol L-1
D) 1.2 × 10-1 mol L-1
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nitrogen dioxide decomposes at 300 °C via a second-order process to produce nitrogen monoxide and oxygen according to the following chemical equation: 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) . A sample of NO2(g) is initially placed in a 2.50 L reaction vessel at 300 °C.If the half-life and the rate constant at 300 °C are 11 seconds and 0.54 L mol-1 s-1,respectively,how many moles of NO2 were in the original sample?
A) 0.17 mol
B) 0.42 mol
C) 5.9 mol
D) 15 mol
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the rate constant at 305 K for the reaction: 2 N2O5 → 2 N2O4 + O2, If k = 3.46 × 10-5 s-1 at 298 K and Ea = 106 kJ/mol?
A) 2.4 × 10-5 s-1
B) 4.8 × 10-5 s-1
C) 6.0 × 10-5 s-1
D) 1.2 × 10-5 s-1
E) 9.2 × 10-5 s-1
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a reaction that follows the general rate law,Rate = k[A][B]2,what will happen to the rate of reaction if the concentration of A is increased by a factor of 5.00?
A) The rate will decrease by a factor of 1/25.0.
B) The rate will decrease by a factor of 1/5.00.
C) The rate will increase by a factor of 5.00.
D) The rate will increase by a factor of 25.0.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction: 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) concentration-time data are:
![For the reaction: 2 NO<sub>2</sub>(g) → 2 NO(g) + O<sub>2</sub>(g) concentration-time data are: What is the order of the reaction with respect to [NO<sub>2</sub>]? A) zero B) first C) second D) third E) 2 + 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/11ec76be_a763_ec83_9e6f_b182274362fd_TB5343_00.jpg) What is the order of the reaction with respect to [NO2]?
What is the order of the reaction with respect to [NO2]?
A) zero
B) first
C) second
D) third
E) 2 + 2
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Substance A decomposes by a first-order reaction.Starting initially with [A] = 2.00 M,after 150 min [A] = 0.50 M.For this reaction what is ![Substance A decomposes by a first-order reaction.Starting initially with [A] = 2.00 M,after 150 min [A] = 0.50 M.For this reaction what is ? A) 150 min B) 37.5 min C) 75.0 min D) 15.0 min E) 300 min](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/11ea7a5e_3e7e_c0b9_89bd_19c8b3096e93_TB5343_11.jpg) ?
?
A) 150 min
B) 37.5 min
C) 75.0 min
D) 15.0 min
E) 300 min
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Define rate law.
A) A theoretical equation that describes how the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants.
B) An experimentally determined equation that describes how the rate of reaction depends on the concentration of reactants.
C) A theoretical equation that describes how the rate of reaction depends on temperature,orientation and number of collisions.
D) An experimentally determined equation that describes how the rate of reaction depends on temperature,orientation and number of collisions.
E) A statement that describes how the ratio of reaction depends on concentration of reactants developed from the balanced equation.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is FALSE for a second order reaction?
A) 1/[A]t - 1/[A]o = kt.
B) t1/2 = 1/k[A]o.
C) If 1/[A] versus time is a straight line,the reaction is second order.
D) Each successive half-life is 4 times as long as the previous.
E) The slope of 1/[A]t versus time is k.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the INCORRECT answer.The rate of a chemical reaction:
A) usually is increased when the concentration of one of the reactants is increased
B) is dependent on temperature
C) may be increased by certain catalytic agents
D) will be very rapid if the activation energy is large
E) describes the rate of change in concentration of a reactant or product with time
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the second-order reaction A → products,the following data are obtained: [A] = 1.512 M,t = 0 min [A] = 1.490 M,t = 1.0 min [A] = 1.469 M,t = 2.0 min What is the initial rate of the reaction in the experiment?
A) 0.40 M/min
B) 0.022 M/min
C) 0.089 M/min
D) 9.8 × 10-3 M/min
E) 0.046 M/min
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a catalyst is added to a reaction: I.the value of k is increased II.the value of k is decreased III.the rate is increased IV.the rate is decreased V.neither rate nor the constant are changed,only the order
A) I and IV
B) II and IV
C) II and III
D) I and III
E) V only
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If increasing the concentration of A in a chemical reaction causes no increase in the rate of the reaction,then we may say the reaction rate is first order in [A].
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
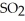
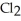 Decomposes in the gas phase by the reaction
Decomposes in the gas phase by the reaction 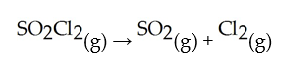 The reaction is first order in
The reaction is first order in 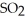
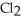 And the rate constant is 3.0 ×
And the rate constant is 3.0 × 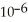
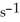 At 600 K.A vessel is charged with 2.4 atm of
At 600 K.A vessel is charged with 2.4 atm of 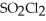 At 600 K.The partial pressure of
At 600 K.The partial pressure of 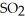
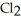 At
At 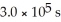 Is ________ atm.
Is ________ atm.
A) 0.76
B) 2.2
C) 0.98
D) 0.29
E) 1.4 × 105
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the half-life of a reactant is independent of its initial concentration,the reaction order is 0.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has no effect on the rate of a reaction?
A) value of ΔH°
B) activation energy
C) presence of a catalyst
D) temperature of reactants
E) concentrations of reactants
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction: 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g) the rate law is:
![For the reaction: 2 N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>(g) → 4 NO<sub>2</sub>(g) + O<sub>2</sub>(g) the rate law is: = k[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>] At 300 K,the half-life is 2.50 × 10<sup>4</sup> seconds and the activation energy is 103.3 kJ/mol O<sub>2</sub>.What is the half-life at 350 K? A) 67.3 s B) 9.3 × 10<sup>6</sup> s C) 1.09 × 10<sup>-17</sup> s D) 2.48 × 10<sup>4</sup> s E) 0.145 s](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/11ea7a5e_3e7f_35eb_89bd_759a15a569c6_TB5343_11.jpg) = k[N2O5]
At 300 K,the half-life is 2.50 × 104 seconds and the activation energy is 103.3 kJ/mol O2.What is the half-life at 350 K?
= k[N2O5]
At 300 K,the half-life is 2.50 × 104 seconds and the activation energy is 103.3 kJ/mol O2.What is the half-life at 350 K?
A) 67.3 s
B) 9.3 × 106 s
C) 1.09 × 10-17 s
D) 2.48 × 104 s
E) 0.145 s
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The isomerization reaction,CH3NC → CH3CN,is first order and the rate constant is equal to 0.46 s-1 at 600 K.What is the concentration of CH3NC after 0.20 minutes if the initial concentration is 0.30 mol L-1?
A) 1.2 × 10-3 mol L-1
B) 2.7 × 10-3 mol L-1
C) 1.2 × 10-1 mol L-1
D) 2.7 × 10-1 mol L-1
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For 2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2,initial rate data are:
![For 2 NO + O<sub>2</sub> → 2 NO<sub>2</sub>,initial rate data are: The rate law is Rate = k[NO][O<sub>2</sub>]<sup>y</sup>: A) x = 1,y = 2 B) x = 2,y = 1 C) x = 1,y = 1 D) x = 2,y = 2 E) x = 0,y = 2](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/11ec76bc_fc69_6f8c_9e6f_1593860de59a_TB5343_00.jpg) The rate law is Rate = k[NO][O2]y:
The rate law is Rate = k[NO][O2]y:
A) x = 1,y = 2
B) x = 2,y = 1
C) x = 1,y = 1
D) x = 2,y = 2
E) x = 0,y = 2
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In aqueous solution,hypobromite ion,BrO-,reacts to produce bromate ion,BrO3-,and bromide ion,Br-,according to the following chemical equation:
![In aqueous solution,hypobromite ion,BrO<sup>-</sup>,reacts to produce bromate ion,BrO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>,and bromide ion,Br<sup>-</sup>,according to the following chemical equation: A plot of 1/[BrO<sup>-</sup>] vs.time is linear and the slope is equal to 0.056 L mol<sup>-1 </sup>s<sup>-1</sup>.If the initial concentration of BrO<sup>-</sup> is 0.80 mol L<sup>-1</sup>,how long will it take one-half of the BrO<sup>- </sup>ion to react? A) 4.5 × 10<sup>-2</sup> s B) 7.1 s C) 12 s D) 22 s](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/11ea7a5e_3e82_1b62_89bd_45d97ead969c_TB5343_11.jpg) A plot of 1/[BrO-] vs.time is linear and the slope is equal to 0.056 L mol-1 s-1.If the initial concentration of BrO- is 0.80 mol L-1,how long will it take one-half of the BrO- ion to react?
A plot of 1/[BrO-] vs.time is linear and the slope is equal to 0.056 L mol-1 s-1.If the initial concentration of BrO- is 0.80 mol L-1,how long will it take one-half of the BrO- ion to react?
A) 4.5 × 10-2 s
B) 7.1 s
C) 12 s
D) 22 s
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about the reaction 2 A → B + C which is first order in A and first order overall?
A) The rate of the reaction will decrease at higher concentrations of B and C.
B) The time required for one half of A to react is directly proportional to the quantity of A.
C) The rate of formation of C is twice the rate of reaction of A.
D) The rate of formation of B is the same as the rate of reaction of A.
E) The initial rate doubles with doubling of initial concentration of A.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 124
Related Exams