A) As long as the government establishes the correct price.
B) Because technology is constantly improving.
C) If prices are flexible and free to change.
D) If trade barriers protect domestic production.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following explanations of the business cycle focuses on both aggregate supply and aggregate demand shifts?
A) Monetarist explanations
B) Keynesian explanations
C) Supply-side explanations
D) Eclectic explanations
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unlike the Classical economists,Keynes asserted that:
A) Laissez-faire would lead to macro equilibrium.
B) The economy was inherently unstable.
C) Markets would naturally self-adjust.
D) Wages and prices were flexible.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Keynes believed that small disturbances in the economy would be made even greater by the market mechanism and thus government intervention was required.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is definitely true if the economy is in macro equilibrium?
A) The price level is optimal,but the output level may not be
B) The output level is optimal,but the price level may not be
C) The price level and the output level are both optimal
D) The price level and the output level may or may not be optimal
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynes:
A) Small disturbances in prices and output are always short term.
B) The economy is inherently stable.
C) Government intervention in the economy is necessary at times.
D) High unemployment is always a temporary situation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following economic theories focus on aggregate demand to explain changes in unemployment and inflation?
A) Classical and supply-side
B) Keynesian and monetarist
C) Classical and Keynesian
D) Classical but not monetarist
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following causes the aggregate supply curve to shift to the left,ceteris paribus?
A) An increase in the cost of labor
B) A decrease in the money supply
C) An increase in government spending on goods
D) A decrease in interest rates
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetary policy:
A) Is controlled by Congress.
B) Refers to the use of government spending.
C) Shifts the aggregate supply curve.
D) Is controlled by the Federal Reserve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynesian theory,the correct fiscal policy action to stimulate the economy would be to:
A) Raise taxes to increase aggregate demand.
B) Increase the money supply to increase aggregate supply.
C) Increase government expenditures to increase aggregate demand.
D) Increase education spending to increase aggregate supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ceteris paribus,a rightward shift of the aggregate supply curve will cause the equilibrium price level to _______ and equilibrium real output to _______.
A) Increase;increase
B) Increase;decrease
C) Decrease;increase
D) Decrease;decrease
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes viewed the economy as inherently unstable and suggested that during a recession policy makers should:
A) Cut taxes and/or increase government spending.
B) Cut taxes and/or reduce government spending.
C) Raise taxes and/or increase government spending.
D) Raise taxes and/or reduce government spending.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11.1-Aggregate supply and demand 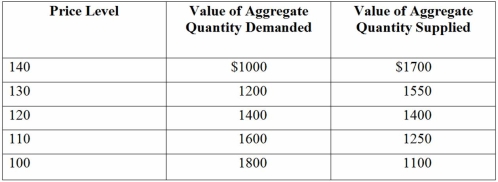 -In Table 11.1,at which of the following price levels would a surplus occur?
-In Table 11.1,at which of the following price levels would a surplus occur?
A) 100
B) 110
C) 120
D) 130
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ceteris paribus,based on the real balances effect,if the price level falls:
A) Wealth decreases.
B) Purchasing power increases.
C) Real income decreases.
D) Business profits increase.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Controversies between Keynesian,monetarist,supply-side,and eclectic theories focus on:
A) The shape and sensitivity of aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves.
B) The existence or nonexistence of the aggregate supply curve.
C) The importance of international balances to the economy.
D) The usefulness of aggregate demand and supply in analyzing macro equilibrium.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because,ceteris paribus:
A) People are willing and able to buy more goods and services at lower average prices.
B) People buy fewer goods and services at lower average incomes.
C) A higher average price level induces producers to offer more output.
D) A higher average price level causes incomes to increase.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy is experiencing a recession,the Keynesian approach to achieving full employment is to:
A) Follow a policy of laissez faire.
B) Relax immigration standards.
C) Reduce government regulations.
D) Use tax cuts or more government spending or both.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For macro equilibrium to occur,aggregate demand must equal aggregate supply at a fairly low price level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between market demand and aggregate demand is that:
A) Market demand applies to all individuals,and aggregate demand does not.
B) Aggregate demand applies to a specific good,and market demand does not.
C) Policy levers work through market demand but not aggregate demand.
D) Aggregate demand applies to all goods and market demand applies to a specific good.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If,at the prevailing price level,the aggregate quantity supplied exceeds the aggregate quantity demanded,the price level will tend to fall.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 149
Related Exams