B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
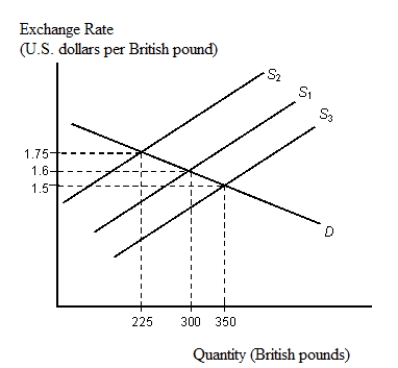 -When a U.S. importer needs $22,000 to settle an invoice for 25,520 Swiss francs, the exchange rate must be:
-When a U.S. importer needs $22,000 to settle an invoice for 25,520 Swiss francs, the exchange rate must be:
A) 1 Swiss franc = $1.16.
B) 1 Swiss franc = $0.16.
C) 1 Swiss franc = $0.84.
D) $1 = 1.16 Swiss franc.
E) $1 = 1.84 Swiss franc.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Assume that a Chrysler automobile sells for $15,000 in the United States and that the exchange rate is $1 = €1.3. For purchasing power parity to hold, the same car should sell in Germany for:
-Assume that a Chrysler automobile sells for $15,000 in the United States and that the exchange rate is $1 = €1.3. For purchasing power parity to hold, the same car should sell in Germany for:
A) €15,000.
B) €11,538.
C) €19,500.
D) €1,538.
E) €15,500.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -The euro floats against other currencies, but the member nations of the euro have no separate national money. For this reason, Spain, that uses the euro as its currency is listed under the managed float arrangement.
-The euro floats against other currencies, but the member nations of the euro have no separate national money. For this reason, Spain, that uses the euro as its currency is listed under the managed float arrangement.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
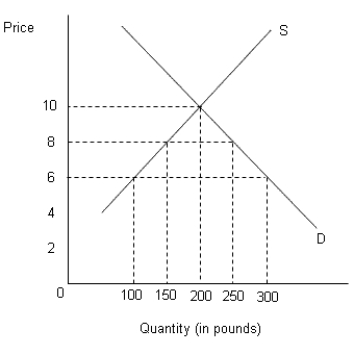 -The U.S. provides about _____ percent of the annual membership fees of IMF member countries.
-The U.S. provides about _____ percent of the annual membership fees of IMF member countries.
A) 5.6
B) 10.2
C) 15.3
D) 17.3
E) 22.4
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
 -The focal point of the Bretton Woods system was the:
-The focal point of the Bretton Woods system was the:
A) Great Britain pound.
B) institution of special drawing rights.
C) U.S. dollar.
D) gold reserve.
E) management of commodity money.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Assume a U.S. investor buys a Mexican bond with a face value of MXP 1,000 and a 20 percent annual interest yield while the exchange rate is MXP 10 per dollar. What is the dollar return from the bond if the exchange rate at the end of the year is MXP 11 per dollar?
-Assume a U.S. investor buys a Mexican bond with a face value of MXP 1,000 and a 20 percent annual interest yield while the exchange rate is MXP 10 per dollar. What is the dollar return from the bond if the exchange rate at the end of the year is MXP 11 per dollar?
A) 9.1%
B) 10.0%
C) 18.2%
D) 20.0%
E) 32.0%
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Suppose a permanent increase in demand for the Argentinean peso causes a chronic shortage of this currency in the foreign exchange market. The Argentinean government should then:
-Suppose a permanent increase in demand for the Argentinean peso causes a chronic shortage of this currency in the foreign exchange market. The Argentinean government should then:
A) request other countries to revalue their currency.
B) devalue the peso.
C) allow the peso to appreciate.
D) restricts exports.
E) restrict imports.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Suppose the yen value of a $100,000 wheat import contract rises from ¥12,000,000 to ¥13,000,000 between the contract and the payment date. This implies that the yen value of 1 dollar has declined so that, other things equal, we can expect an increase in Japanese demand for U.S. goods.
-Suppose the yen value of a $100,000 wheat import contract rises from ¥12,000,000 to ¥13,000,000 between the contract and the payment date. This implies that the yen value of 1 dollar has declined so that, other things equal, we can expect an increase in Japanese demand for U.S. goods.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the demand and supply of Brazilian reals in the foreign exchange market. Assume that the market operates under a flexible exchange rate regime.Figure 22.1
In the figure:
D1 and D2: Demand for Brazilian reals
S1 and S2: Supply of Brazilian reals
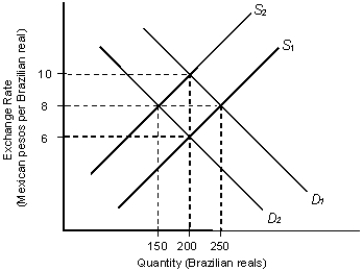 -Refer to Figure 22.1. Suppose the initial equilibrium exchange rate is 10 pesos per real. A decrease in the Mexican demand for Brazilian coffee, other things equal, is most likely to result in a new equilibrium exchange rate of:
-Refer to Figure 22.1. Suppose the initial equilibrium exchange rate is 10 pesos per real. A decrease in the Mexican demand for Brazilian coffee, other things equal, is most likely to result in a new equilibrium exchange rate of:
A) 6 pesos per real and an equilibrium quantity of 200 Brazilian reals.
B) 6 pesos per real and an equilibrium quantity of 250 Brazilian reals.
C) 8 pesos per real and an equilibrium quantity of 150 Brazilian reals.
D) 8 pesos per real and an equilibrium quantity of 100 Brazilian reals.
E) 10 pesos per real and an equilibrium quantity of 200 Brazilian reals.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
 -Under the Bretton Woods system, international debts were settled in:
-Under the Bretton Woods system, international debts were settled in:
A) gold.
B) U.S. dollars.
C) British pounds.
D) silver.
E) German marks.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the demand and supply of Brazilian reals in the foreign exchange market. Assume that the market operates under a flexible exchange rate regime.Figure 22.1
In the figure:
D1 and D2: Demand for Brazilian reals
S1 and S2: Supply of Brazilian reals
 -Refer to Figure 22.1. The demand curves shown for Brazilian reals are based on:
-Refer to Figure 22.1. The demand curves shown for Brazilian reals are based on:
A) the supply of Brazilian reals in the market.
B) the demand for Mexican pesos.
C) Brazilian demand for Brazilian products.
D) Brazilian demand for Mexican products.
E) Mexican demand for Brazilian products.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -If a bushel of corn sells for $2 in the United States and for 4,000 COP (Colombian peso) in Colombia, and if 1 dollar is worth 2,200 COP, then:
-If a bushel of corn sells for $2 in the United States and for 4,000 COP (Colombian peso) in Colombia, and if 1 dollar is worth 2,200 COP, then:
A) the corn is 400 COP more expensive in Colombia.
B) the corn is 400 COP cheaper in Colombia.
C) the price of a bushel of corn equals $2 in both the United States and Colombia.
D) the price of corn is 4,000 COP lower in Colombia than in the United States.
E) the price of corn is $0.20 lower in the United States than in Colombia.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the demand and supply of Brazilian reals in the foreign exchange market. Assume that the market operates under a flexible exchange rate regime.Figure 22.1
In the figure:
D1 and D2: Demand for Brazilian reals
S1 and S2: Supply of Brazilian reals
 -The supply of Thai baht in the foreign exchange market originates with:
-The supply of Thai baht in the foreign exchange market originates with:
A) tourists who go on vacation to Thailand.
B) the export of Thai oranges and other goods.
C) Thai residents who wish to purchase goods from other countries.
D) the Thai royal family.
E) Thai central bank intervention to stop the peseta from depreciating.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Which of the following holds true, if goods sell for the same price worldwide when converted to a common currency?
-Which of the following holds true, if goods sell for the same price worldwide when converted to a common currency?
A) A high rate of inflation exists.
B) A fixed exchange-rate system exists.
C) Purchasing power parity exists.
D) The foreign exchange market is in equilibrium.
E) Arbitrage opportunities exist.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Under both the gold standard and the gold exchange standard countries bought and sold U.S. dollars to maintain a fixed exchange rate with the dollar.
-Under both the gold standard and the gold exchange standard countries bought and sold U.S. dollars to maintain a fixed exchange rate with the dollar.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -Suppose a U.S. citizen invests $1,000 to purchase a one-year Japanese bond that has an interest yield of 10 percent. If the dollar appreciates 20 percent against the Japanese yen by the maturity date, the dollar value of the proceeds is _____.
-Suppose a U.S. citizen invests $1,000 to purchase a one-year Japanese bond that has an interest yield of 10 percent. If the dollar appreciates 20 percent against the Japanese yen by the maturity date, the dollar value of the proceeds is _____.
A) $900
B) $1,100
C) $1,300
D) $1,500
E) $1,200
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
 -What is a currency board?
-What is a currency board?
A) A fixed exchange rate that, by law, exchanges domestic currency for a specified foreign currency at a fixed exchange rate.
B) A floating exchange rate.
C) A managed floating exchange-rate policy that the government adjusts periodically according to some economic indicator.
D) A laissez-faire exchange-rate policy.
E) An interventionist exchange-rate policy.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The figure given below depicts the foreign exchange market for British pounds traded for U.S. dollars.Figure 22.2
 -The World Bank was created to help finance economic development in poor countries.
-The World Bank was created to help finance economic development in poor countries.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
 -Assume that a country's government influences the exchange rate through active central bank intervention, with no pre-announced path for the exchange rate. This policy is known as a(n) :
-Assume that a country's government influences the exchange rate through active central bank intervention, with no pre-announced path for the exchange rate. This policy is known as a(n) :
A) floating exchange-rate policy.
B) managed floating exchange-rate policy.
C) fixed exchange-rate policy.
D) crawling-peg exchange-rate policy.
E) interventionist exchange-rate policy.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 130
Related Exams