A) competitive exclusion
B) resource partitioning
C) character displacement
D) keystone species
E) bottom-up and top-down hypotheses
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is a pathogen generally more virulent in a new habitat?
A) More pathogens tend to immigrate into newer habitats.
B) Intermediate host species are more motile and transport pathogens to new areas.
C) Pathogens evolve more efficient forms of reproduction in new environments.
D) Hosts in new environments have not had a chance to become resistant to the pathogen through natural selection.
E) New environments are almost always smaller in area, so that transmission of pathogens is easily accomplished between hosts.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As you study two closely related predatory insect species, the two-spot and the three-spot avenger beetles, you notice that each species seeks prey at dawn in areas without the other species. However, where their ranges overlap, the two-spot avenger beetle hunts at night and the three-spot hunts in the morning. When you bring them into the laboratory and isolate the two different species, you discover that the offspring of both species are found to be nocturnal. You have discovered an example of
A) mutualism.
B) character displacement.
C) Batesian mimicry.
D) facultative commensalism.
E) resource partitioning.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What interactions exist between a bee and a flower?
A) +/+
B) +/o
C) +/-
D) o/o
E) -/-
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please refer to Figure 41.2 to answer the following question.
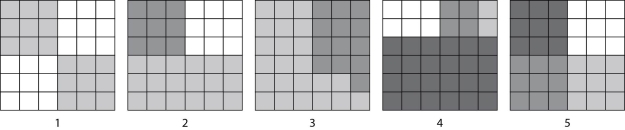 Figure 41.2
-According to the Shannon Diversity Index, which block would show the greatest diversity?
Figure 41.2
-According to the Shannon Diversity Index, which block would show the greatest diversity?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of cryptic coloration?
A) bands on a coral snake
B) brown or gray color of tree bark
C) markings of a viceroy butterfly's wings
D) colors of an insect-pollinated flower's petals
E) a "walking stick" insect that resembles a twig
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the diagram in Figure 41.4 of five islands formed at around the same time near a particular mainland, as well as MacArthur and Wilson's island biogeography principles, to answer the following questions.
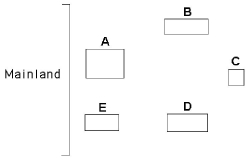 Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely exhibit the most impoverished species diversity?
Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely exhibit the most impoverished species diversity?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to bottom-up and top-down control models of community organization, which of the following expressions would imply that an increase in the size of a carnivore (C) population would negatively impact on its prey (P) population, but not vice versa?
A) P ← C
B) P → C
C) C ↔ P
D) P ← C → P
E) C ← P →
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is consistent with the principle of competitive exclusion?
A) Bird species generally do not compete for nesting sites.
B) The random distribution of one competing species will have a positive impact on the population growth of the other competing species.
C) Two species with the same fundamental niche will exclude other competing species.
D) Even a slight reproductive advantage will eventually lead to the elimination of the less well adapted of two competing species.
E) Natural selection tends to increase competition between related species.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the diagram of a hypothetical food web in Figure 41.3 to answer the following questions. The arrows represent the transfer of energy between the various trophic levels.
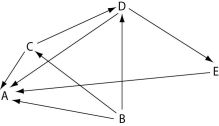 Figure 41.3
-Which letter represents an organism that could be a primary producer?
Figure 41.3
-Which letter represents an organism that could be a primary producer?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a particular case of secondary succession, three species of wild grass all invaded a field. By the second season, a single species dominated the field. A possible factor in this secondary succession was
A) equilibrium.
B) facilitation.
C) immigration.
D) inhibition.
E) parasitism.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct statement about the McArthur/Wilson Island Equilibrium Model?
A) The more species that inhabit an island, the lower the extinction rate.
B) As the number of species on an island increases, the emigration rate decreases.
C) Competitive exclusion is less likely on an island that has large numbers of species.
D) Small islands receive few new immigrant species.
E) Islands closer to the mainland have higher extinction rates.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dwarf mistletoes are flowering plants that grow on certain forest trees. They obtain nutrients and water from the vascular tissues of the trees. The trees derive no known benefits from the dwarf mistletoes. Which of the following best describes the interactions between dwarf mistletoes and trees?
A) mutualism
B) parasitism
C) commensalism
D) facilitation
E) competition
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What interactions exist between a tick on a dog and the dog?
A) +/+
B) +/o
C) +/-
D) o/o
E) -/-
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How did Eugene Odum describe an ecological niche?
A) the "address" of an organism
B) an entity that is synonymous with an organism's specific trophic level
C) an organism's "profession" in the community
D) the organism's role in recycling nutrients in its habitat
E) the interactions of the organism with other members of the community
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following could qualify as a top-down control on a grassland community?
A) limitation of plant biomass by rainfall amount
B) influence of temperature on competition among plants
C) influence of soil nutrients on the abundance of grasses versus wildflowers
D) effect of grazing intensity by bison on plant species diversity
E) effect of humidity on plant growth rates
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the diagram in Figure 41.4 of five islands formed at around the same time near a particular mainland, as well as MacArthur and Wilson's island biogeography principles, to answer the following questions.
 Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely have the greatest species diversity?
Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely have the greatest species diversity?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The oak tree pathogen Phytophthora ramorum has migrated 800 km in 15 years. West Nile virus spread from New York State to 46 other states in 5 years. The difference in the rate of spread is probably related to
A) the lethality of each pathogen.
B) the mobility of their hosts.
C) the fact that viruses are very small.
D) innate resistance.
E) dormancy viability.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine five forest communities, each with 100 individuals distributed among four different tree species (W, X, Y, and Z) . Which forest community would be most diverse?
A) 25W, 25X, 25Y, 25Z
B) 40W, 30X, 20Y, 10Z
C) 50W, 25X, 15Y, 10Z
D) 70W, 10X, 10Y, 10Z
E) 100W, 0X, 0Y, 0Z
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the diagram in Figure 41.4 of five islands formed at around the same time near a particular mainland, as well as MacArthur and Wilson's island biogeography principles, to answer the following questions.
 Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely have the lowest extinction rate?
Figure 41.4
-Which island would likely have the lowest extinction rate?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 55
Related Exams