A) protein
B) fat
C) nucleic acids
D) carbohydrates
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Coprophagy is important for the nutritional balance of ________.
A) ruminants such as cows
B) insects and arthropods
C) rabbits and their relatives
D) possums and some rodents
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of obtaining food is known as ________ and requires specialised feeding mechanisms.
A) ingestion
B) digestion
C) absorption
D) excretion
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cattle are able to survive on a diet consisting almost entirely of plant material because cattle ________.
A) are autotrophic
B) re-ingest their faeces
C) manufacture all 15 amino acids out of sugars in the liver
D) have cellulose-digesting, symbiotic microorganisms in chambers of their stomachs
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. 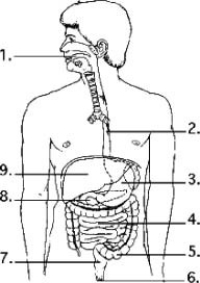 -The agents that help emulsify fats are produced in location ________.
-The agents that help emulsify fats are produced in location ________.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 8
D) 9
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the importance of the mucus that are released by salivary glands?
A) They aid in degradation of triglycerides to fatty acids and monoglycerides.
B) They are beginning the process of starch digestion.
C) They are hormonal molecules that stimulate the release of gastric juice by the stomach in anticipation of receipt of the contents of the mouth.
D) They are glycoproteins that make food slippery enough to slide easily through the oesophagus.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals that migrate great distances would obtain the greatest energetic benefit of storing chemical energy as ________.
A) proteins
B) minerals
C) carbohydrates
D) fats
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An advantage of a complete digestive system over a gastrovascular cavity is that the complete system ________.
A) excludes the need for extracellular digestion
B) allows for specialised regions with specialised functions
C) allows extensive branching
D) facilitates intracellular digestion
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Among mammals, it is generally true that ________.
A) all types of foods begin their enzymatic digestion in the mouth
B) after leaving the oral cavity, the bolus enters the larynx
C) the epiglottis prevents swallowed food from entering the trachea
D) the trachea leads to the oesophagus and then to the stomach
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The large surface area in the gut directly facilitates ________.
A) secretion
B) absorption
C) filtration
D) temperature regulation
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you found a vertebrate skull in the bush and the teeth were sharp and scissor-like, what type of food would you expect this animal to eat?
A) grass
B) flesh of another animal
C) nectar
D) blood
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a hydra, digestion is completed ________.
A) intracellularly
B) extracellularly
C) in the alimentary canal
D) in the gastrovascular cavity
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Upon activation by stomach acidity, the secretions of the parietal cells ________.
A) initiate the chemical digestion of protein in the stomach
B) initiate the mechanical digestion of lipids in the stomach
C) initiate the chemical digestion of lipids in the stomach
D) delay digestion until the food arrives in the small intestine
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The active ingredient orlistat acts to decrease the amount of fat that is absorbed by attaching to enzymes that digest fat. Which of the following are potential targets of orlistat?
A) salivary amylase
B) pepsidase
C) pancreatic lipase
D) secretin
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were to jog one kilometre a few hours after lunch, which stored fuel would you probably tap?
A) muscle proteins
B) liver glycogen and muscle glycogen
C) fat stored in adipose tissue
D) blood proteins
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. 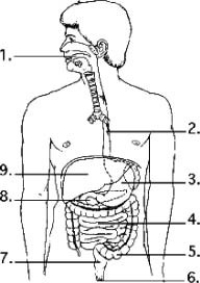 -Most of the digestion of fats occurs in structure(s) ________.
-Most of the digestion of fats occurs in structure(s) ________.
A) 3 only
B) 4 only
C) 1 and 4
D) 3 and 4
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the digestion and absorption of organic carbohydrates results in more energy-rich molecules than are immediately required by an animal, the excess is ________.
A) eliminated in the faeces
B) stored as starch in the liver
C) stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles
D) oxidised and converted to ATP
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do the cells of the digestive system secrete proteolytic enzymes, such as pepsin, in their inactive forms?
A) These proteolytic enzymes, in active form, would digest the very tissues that synthesise them.
B) By secreting inactive enzymes, the catalytic activity of the enzymes is maintained for a longer time.
C) The stomach is too acidic to maintain these enzymes in their active form.
D) Inactive pepsin and trypsin are more easily transported across the cell membrane.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fasting animal whose energy needs exceed those provided in its diet will draw on its stored resources in which order?
A) fat, then glycogen, then protein
B) glycogen, then protein, then fat
C) liver glycogen, then muscle glycogen, then fat
D) muscle glycogen, then fat, then liver glycogen
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A significant contribution of intestinal bacteria to human nutrition is the benefit of bacterial ________.
A) production of vitamins A and C
B) absorption of organic materials
C) production of vitamin K
D) recovery of water from faecal matter
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 64
Related Exams