A) there are no dedicated hormone-producing organs in plants as there are in animals
B) all production of hormones is local in plants with little long-distance transport
C) only animal hormone concentrations are developmentally regulated
D) only animal hormones may have either external or internal receptors
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the autumn, the leaves of some trees change colour. This happens because chlorophyll breaks down and the accessory pigments become visible. What hormone is responsible for this?
A) phototropin
B) abscisic acid
C) cytokinin
D) ethylene
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seed packets give a recommended planting depth for the enclosed seeds. The most likely reason some seeds are to be covered with only ½ centimetre of soil is that the ________.
A) seedlings do not have an etiolation response
B) seeds require light to germinate
C) seeds require a higher temperature to germinate
D) seeds are very sensitive to waterlogging
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In extremely cold regions, woody species may survive freezing temperatures by ________.
A) emptying water from the vacuoles to prevent freezing
B) decreasing the numbers of phospholipids in cell membranes
C) decreasing the fluidity of all cellular membranes
D) increasing cytoplasmic levels of specific solute concentrations, such as sugars
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ prevents seeds from germinating until conditions are favourable for the growth of the plant.
A) Ethylene
B) Zeaxanthin
C) Gibberellin
D) Abscisic acid
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which event during the evolution of land plants favoured the synthesis of secondary compounds?
A) the greenhouse effect throughout the Devonian period
B) the reverse-greenhouse effect during the Carboniferous period
C) the association of the roots of land plants and fungi
D) the rise of herbivory
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant scientist was hired by a greenhouse operator to devise a way to force iris plants to bloom in the short days of winter. Iris normally blooms as a long-day (short-night) plant. Which of the following has the best chance of creating iris blooms in winter?
A) Artificially increase the period of darkness in the greenhouse.
B) Increase the temperature to more closely follow summer temperatures.
C) Alternate four hours of darkness with four hours of light repeatedly over each 24-hour period.
D) Interrupt the long winter nights with a brief period of light.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were shipping green bananas to a supermarket thousands of miles away, which of the following chemicals would you want to eliminate from the plants' environment?
A) carbon dioxide
B) cytokinins
C) ethylene
D) auxin
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
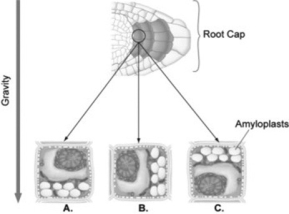 Suppose you laid a seedling on its side so that the root was parallel to the ground as shown in the figure. Several hours after the change in position, where in the root cells, position A, B, or C in the figure, would you find the amyloplasts?
Suppose you laid a seedling on its side so that the root was parallel to the ground as shown in the figure. Several hours after the change in position, where in the root cells, position A, B, or C in the figure, would you find the amyloplasts?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) A and C
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most scientists agree that global warming is underway; thus, it is important to know how plants respond to heat stress. Which of the following would be a useful line of inquiry to try and improve plant response and survival to heat stress?
A) the production of heat-stable carbohydrates
B) increased production of heat-shock proteins
C) the opening of stomata to increase evaporational heat loss
D) protoplast fusion experiments with xerophytic plants
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Apical dominance in plants is under the control of ________.
A) sugar
B) various plant hormones
C) cell division
D) sugar and various plant hormones
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plant hormones ________.
A) in plant cells naturally exist in very large amounts
B) change their shape in response to stimulus
C) are unable to move from one cell to another
D) affect only cells with the appropriate receptor
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gardener in Canada wants to surprise his mother on her birthday and make her favourite hibiscus bush flower in May instead of at the end of June. The bush is growing in the greenhouse. Which of the following might make the hibiscus bush flower early?
A) grafting leaves of a hibiscus that was exposed to long nights
B) grafting leaves of a hibiscus that was exposed to short nights
C) exposing flower buds of the hibiscus bush to long nights
D) exposing flower buds of the hibiscus bush to short nights
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Auxin enhances cell elongation in all of these ways except
A) increased uptake of solutes.
B) gene activation.
C) acid-induced denaturation of cell wall proteins.
D) cell wall loosening.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rapid leaf movements resulting from a response to touch (thigmotropism) primarily involve ________.
A) potassium channels
B) nervous tissue
C) aquaporins
D) stress proteins
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plants often use changes in day length (photoperiod) to trigger events such as dormancy and flowering. It is logical that plants have evolved this mechanism because photoperiod changes ________.
A) are more predictable than air temperature changes
B) predict moisture availability
C) are modified by soil temperature changes
D) can reset the biological clock
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The detector of light during de-etiolation (greening) of a tomato plant is (are) ________.
A) carotenoids
B) xanthophylls
C) phytochrome
D) auxin
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Experiments on the positive phototropic response of plants indicate that ________.
A) light destroys auxin
B) auxin moves down the plant apoplastically
C) auxin is synthesised in the area where the stem bends
D) auxin can move to the shady side of the stem
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a small tree in your yard that is the height that you want it, but does not have as many branches as you want. How can you prune it to trigger it to increase the number of branches?
A) Cut off the leaves at the ends of several branches.
B) Cut off the tips of the main shoots.
C) Cut off lower branches.
D) Cut off the leaves at the base of most of the branches.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of mutant would be most likely to produce a bushier phenotype?
A) auxin overproducer
B) strigolactone overproducer
C) cytokinin underproducer
D) strigolactone underproducer
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 61
Related Exams