A) 8.4%
B) 9.0%
C) 9.2%
D) 35.2%
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Table 28-9
The table below lists the number of people by labor force classification for the country of Shelbyville.
 -Refer to Table 28-9. What is the labor force participation rate?
-Refer to Table 28-9. What is the labor force participation rate?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the wage is kept above the equilibrium wage for any reason, the result is structural unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct formula for calculating the labor force participation rate?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-5
Labor Force Statistics by Age
Suppose people in the adult population in a small country are classified based on their age.
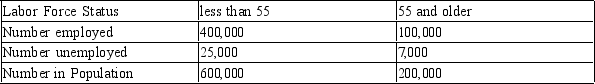 -Refer to Table 28-5. Suppose that the natural rate of unemployment is 5% for those under 55 and 3% for those 55 and older. The cyclical unemployment rate for those under 55 is
-Refer to Table 28-5. Suppose that the natural rate of unemployment is 5% for those under 55 and 3% for those 55 and older. The cyclical unemployment rate for those under 55 is
A) 0.88% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
B) 0.88% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
C) -0.83% which is greater than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
D) -0.83% which is less than the cyclical unemployment rate for those 55 and older.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The labor-force participation rate equals the percentage of the labor force that is either employed or unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics' U4 measure of joblessness includes discouraged workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the past several decades, the difference between the labor-force participation rates of men and women in the U.S. has
A) gradually increased.
B) remained constant.
C) gradually decreased.
D) been eliminated.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) There is consensus among economists that unions are good for the economy.
B) There is consensus among economists that unions are bad for the economy.
C) There is consensus among economists that, on net, unions have almost no impact on macroeconomic variables.
D) There is no consensus among economists about whether unions are good or bad for the economy.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-7
Below is data about the labor market in the city of Productionville.
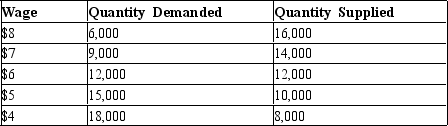 -Refer to Table 28-7. If the local government imposed a minimum wage of $6 in Productionville, how many people would be unemployed?
-Refer to Table 28-7. If the local government imposed a minimum wage of $6 in Productionville, how many people would be unemployed?
A) 0
B) 2,000
C) 3,000
D) 5,000
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) The amount of unemployment that a country typically experiences is a determinant of that country's standard of living, and some degree of unemployment is inevitable in a complex economy.
B) The amount of unemployment that a country typically experiences is a determinant of that country's standard of living, and a complex economy can achieve zero unemployment.
C) The amount of unemployment that a country typically experiences is not a determinant of that country's standard of living, and a complex economy can achieve zero unemployment.
D) The amount of unemployment that a country typically experiences is not a determinant of that country's standard of living, and some degree of unemployment is inevitable in a complex economy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions contribute to
A) frictional unemployment but not the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the natural rate of unemployment but not frictional unemployment.
C) both frictional unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment.
D) neither frictional unemployment nor the natural rate of unemployment.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sam has no job but keeps applying to get a job with a business that is unionized. He is qualified and he finds the pay attractive, but the firm is not hiring. Sam is
A) structurally unemployed. Structural unemployment exists even in the long run.
B) structurally unemployed. Structural unemployment does not exist in the long run.
C) frictionally unemployed. Frictional unemployment exists even in the long run.
D) frictionally unemployed. Frictional unemployment does not exist in the long run.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm may pay efficiency wages in an attempt to
A) reduce incentives to shirk.
B) reduce turnover.
C) attract a well-qualified pool of applicants.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics divides the adult population into two categories: those who are employed and those who are unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-1
Sample Population
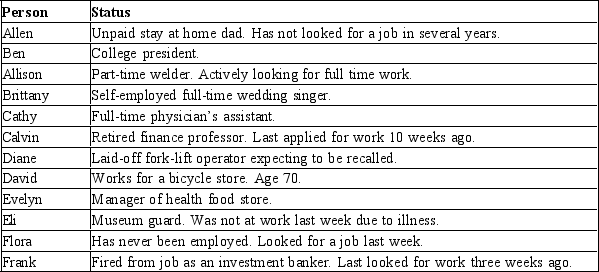 -Refer to Table 28-1. How many in the sample are in the labor force?
-Refer to Table 28-1. How many in the sample are in the labor force?
A) 11
B) 10
C) 9
D) 8
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to 2012 data on the U.S. population, which of the following groups of adults of prime working age ages (25-54) had the lowest labor-force participation rate?
A) white males
B) white females
C) black males
D) black females
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sirius has just finished high school and started looking for his first job, but has not yet found one. Other things the same, the unemployment rate
A) and the labor-force participation rate both increase.
B) increases, and the labor-force participation rate is unaffected.
C) is unaffected, and the labor-force participation rate increases.
D) and the labor-force participation rate are both unaffected.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the theory of efficiency wages, firms operate more efficiently if wages are above the equilibrium level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Belgium, Norway, and Sweden, the percentage of workers who belong to unions is
A) almost zero.
B) less than it is in the United States.
C) about the same as it is in the United States.
D) greater than it is in the United States.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 521 - 540 of 699
Related Exams