A) 400 cubic meters per second
B) 120 cubic meters per second
C) 40 cubic meters per second
D) 22 cubic meters per second
E) 14 cubic meters per second
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pattern of discharge shown by this hydrograph? 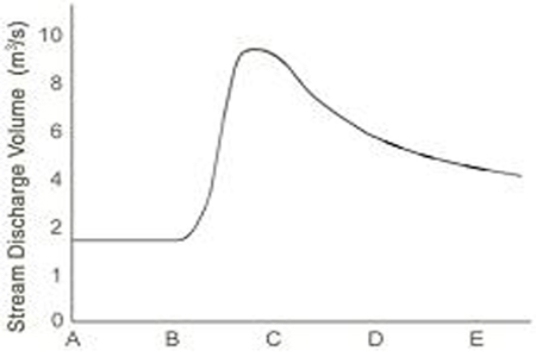
A) Discharge gradually increases and quickly decreases.
B) Discharge quickly increases and gradually decreases.
C) Discharge gradually decreases and quickly increases.
D) Discharges quickly decreases and gradually increases.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the features on this aerial photograph is a point bar? 
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can have a significant effect on a river?
A) rises and drops in sea level
B) tectonics
C) types of bedrock in the river
D) changes in climate
E) All of these.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following features are generally NOT associated with mountain streams and rivers?
A) waterfalls
B) rapids
C) canyons incised into bedrock
D) meanders
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure shows four numbered river terraces, with 1 being the highest and 4 being the lowest.Which is the youngest terrace? 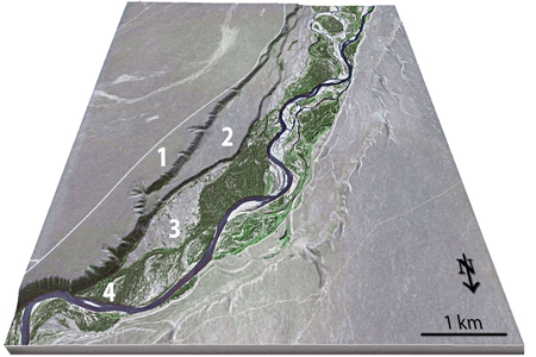
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about levees?
A) They are a reliable way to protect an area from flooding.
B) To be called a levee, a feature needs to be at least partly constructed by humans.
C) A levee can trap water on the floodplain after the flood has subsided.
D) None of these.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would happen if the ice in this area melted away? 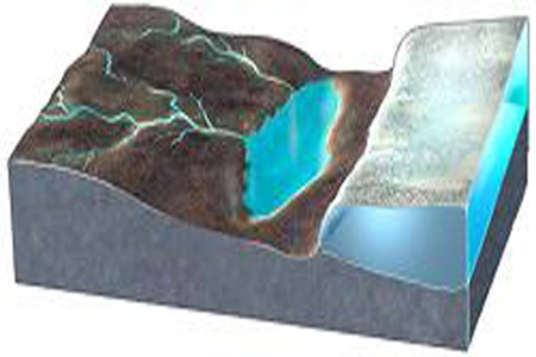
A) The land near the ice would drop due to isostatic rebound.
B) Rivers could change direction and flow away from the area once covered by ice.
C) The land subsides because the ice is removed.
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bedrock and sediment in a stream is most susceptible to erosion if it is
A) in slow-moving water in an eddy.
B) in a site that is sheltered from oncoming clasts.
C) located in a turbulent part of the river.
D) composed entirely of large clasts that affect stream flow.
E) All of these.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following accompanies urbanization (replacing farms and open areas with cities) ?
A) The discharge pattern of streams in the area does not change.
B) Runoff occurs more quickly and produces a higher peak flow.
C) Runoff becomes more spread out in time, increasing the amount of flooding.
D) Runoff becomes more spread out in time, reducing the amount of flooding.
E) None of these.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A delta forms when
A) ocean waves, especially during storms, pile up sediment along the coast.
B) a steep mountain front collapses sending sediment out into the sea.
C) a river slows and deposits sediment as it enters a lake or sea.
D) windblown dust slides down steep hillsides and into a lake.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about a delta?
A) A delta forms as channels merge and pile up sand.
B) A river keeps forming a delta in the exact same position along a coastline.
C) Deltas form some layers that are horizontal and form some that are inclined toward the ocean.
D) The total amount of sediment carried by the river increases from the start to the end of the delta system.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What was the cause of flooding in the 1993 upper Mississippi River flood?
A) Heavy snowmelt in Canada sent large volumes of water down the river in the spring.
B) A dam failed because it had been built in a risky place near a fault.
C) Persistent thunderstorms caused large amounts of rainfall over a several-state region.
D) Winter produced rain that melted snow that was on the ground.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of stream is shown in this figure? 
A) meandering stream
B) braided stream
C) a stream whose main channel has high sinuosity
D) an esker
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lessons was illustrated by flood data from the Colorado River and from the Yellowstone River?
A) Fifty years is a long enough record to record all but a 100-year flood.
B) The largest flood possible along a river is likely to have been witnessed by humans.
C) Few floods are ever larger than 10,000 cubic meters per second.
D) None of these.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do mountain streams get most of their load of sediment?
A) landslides, slope failures, and erosion of the mountain sides
B) downward incision into bedrock
C) abrasion of bedrock along the bottom of the channel
D) alluvial fans
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about transport of sediment in a stream?
A) Pebbles and cobbles are mostly transported by suspension.
B) Sediment that is deposited within a stream bed is unlikely to be transported again.
C) Sand can be transported in a series of bounces along the stream bed.
D) Slower current can carry larger clasts because the water is in contact with each clast for a longer time.
E) Sand grains are converted into salt by the process of saltation.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following influences whether a flood occurs?
A) the height of levees
B) the amount of discharge
C) urbanization (replacing farms or natural land with buildings)
D) the width of the channel
E) All of these are influences.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the mostly likely setting for this drainage pattern? 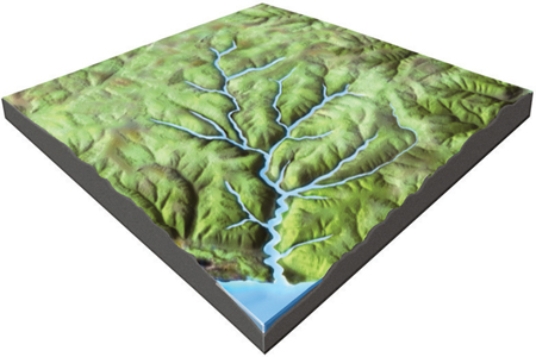
A) The rocks have a relatively equal resistance to erosion.
B) Drainages have followed a series of fractures that branch off of one another.
C) The area has folded or faulted rocks with different resistances to erosion.
D) A volcano once existed here but has been partly eroded away.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What could cause a canyon to be deeper upstream than downstream? 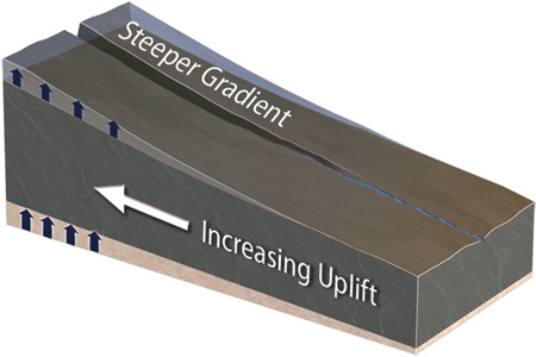
A) The area upstream could be uplifted more than areas downstream.
B) The area upstream is higher above base level and so results in deep erosion.
C) A steeper gradient allows more erosion upstream.
D) All of these.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 95
Related Exams