A) a gravitational force acting on the rocket
B) the force of the exiting fuel gases on the rocket
C) any force that is external to the rocket-fuel system
D) a force that arises from the reduction in mass of the rocket-fuel system
E) none of the above
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1000-kg space probe is motionless in space. To start moving, its main engine is fired for 5 s during which time it ejects exhaust gases at 5000 m/s. At the end of this process it is moving at 20 m/s. The approximate mass of the ejected gas is: 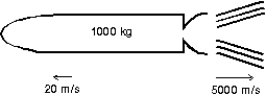
A) 0.8 kg
B) 4 kg
C) 5 kg
D) 20 kg
E) 25 kg
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two carts (A and B) , having spring bumpers, collide as shown. Cart A has a mass of 2 kg and is initially moving to the right. Cart B has a mass of 3 kg and is initially stationary. When the separation between the carts is a minimum: 
A) cart B is still at rest
B) cart A has come to rest
C) the carts have the same momentum
D) the carts have the same kinetic energy
E) the kinetic energy of the system is at a minimum
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inelastic collision is one in which:
A) momentum is not conserved but kinetic energy is conserved
B) total mass is not conserved but momentum is conserved
C) neither kinetic energy nor momentum is conserved
D) momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not conserved
E) the total impulse is equal to the change in kinetic energy
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 500-kg sack of coal is dropped on a 2000-kg railroad flatcar which was initially moving at 3 m/s as shown. After the sack rests on the flatcar, the speed of the flatcar is: 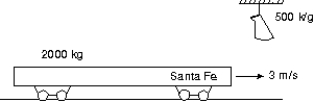
A) 0.6 m/s
B) 1.2 m/s
C) 1.8 m/s
D) 2.4 m/s
E) 3.6 m/s
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two spacemen are floating together with zero speed in a gravity-free region of space. The mass of spaceman A is 120 kg and that of spaceman B is 90 kg. Spaceman A pushes B away from him with B attaining a final speed of 0.5 m/s. The final recoil speed of A is:
A) zero
B) 0.38 m/s
C) 0.5 m/s
D) 0.67 m/s
E) 1.0 m/s
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Blocks A and B are moving toward each other. A has a mass of 2.0 kg and a velocity of 50 m/s, while B has a mass of 4.0 kg and a velocity of -25 m/s. They suffer a completely inelastic collision. The kinetic energy lost during the collision is:
A) 0
B) 1250 J
C) 3750 J
D) 5000 J
E) 5600 J
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 5-kg object can move along the x axis. It is subjected to a force 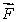 in the positive x direction; a graph of F as a function of time t is shown below. Over the time the force is applied the change in the velocity of the object is:
in the positive x direction; a graph of F as a function of time t is shown below. Over the time the force is applied the change in the velocity of the object is: 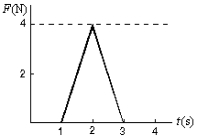
A) 0.8 m/s
B) 1.1 m/s
C) 1.6 m/s
D) 2.3 m/s
E) 4.0 m/s
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the same instant that a 0.50-kg ball is dropped from 25 m above Earth, a second ball, with a mass of 0.25 kg, is thrown straight upward from Earth's surface with an initial speed of 15 m/s. They move along nearby lines and pass without colliding. At the end of 2.0 s the velocity of the center of mass of the two-ball system is:
A) 11 m/s, down
B) 11 m/s, up
C) 15 m/s, down
D) 15 m/s, up
E) 20 m/s, down
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A machinist starts with three identical square plates but cuts one corner from one of them, two corners from the second, and three corners from the third. Rank the three plates according to the x coordinates of their centers of mass, from smallest to largest. 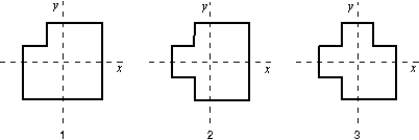
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1 and 2 tie, then 3
C) 1, then 2 and 3 tie
D) 3, 2, 1
E) 1 and 3 tie, then 2
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 4.0-N puck is traveling at 3.0 m/s. It strikes an 8.0-N puck, which is stationary. The two pucks stick together. Their common final speed is:
A) 1.0 m/s
B) 1.5 m/s
C) 2.0 m/s
D) 2.3 m/s
E) 3.0 m/s
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The physical quantity "impulse" has the same dimensions as that of:
A) force
B) power
C) energy
D) momentum
E) work
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When you step on the accelerator to increase the speed of your car, the force that accelerates the car is:
A) the force of your foot on the accelerator
B) the force of friction of the road on the tires
C) the force of the engine on the drive shaft
D) the normal force of the road on the tires
E) none of the above
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a particle suffers a head-on elastic collision with another particle, initially at rest, the greatest fraction of kinetic energy is transferred if:
A) the incident particle is initially traveling very fast
B) the incident particle is traveling very slowly
C) the incident particle is much more massive than the target particle
D) the incident particle is much less massive than the target particle
E) the incident and target particle have the same mass
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The center of mass of a system of particles obeys an equation similar to Newton's second law 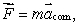 where:
where:
A) ![]() is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total internal force and m is the total mass of the system
B) ![]() is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the system
is the total internal force and m is the mass acting on the system
C) ![]() is the total external force and m is the total mass of the system
is the total external force and m is the total mass of the system
D) ![]() is the force of gravity and m is the mass of Earth
is the force of gravity and m is the mass of Earth
E) ![]() is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
is the force of gravity and m is the total mass of the system
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.0-kg and a 2.0-kg cart approach each other on a horizontal air track. They collide and stick together. After the collision their total kinetic energy is 40 J. The speed of their center of mass is:
A) zero
B) 2.8 m/s
C) 4.0 m/s
D) 5.2 m/s
E) 6.3 m/s
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sphere A has mass m and is moving with velocity v. It makes a head-on elastic collision with a stationary sphere B of mass 2m. After the collision their speeds (vA, and vB) are:
A) 0, v/2
B) -v/3, 2v/3
C) -v, v
D) -2v/3, v/3
E) none of these
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Block A, with a mass of 4 kg, is moving with a speed of 2.0 m/s while block B, with a mass of 8 kg, is moving in the opposite direction with a speed of 3 m/s. The center of mass of the two block-system is moving with the velocity of:
A) 1.3 m/s in the same direction as A
B) 1.3 m/s in the same direction as B
C) 2.7 m/s in the same direction as A
D) 1.0 m/s in the same direction as B
E) 5.0 m/s in the same direction as A
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.0 kg-ball moving at 2.0 m/s perpendicular to a wall rebounds from the wall at 1.5 m/s. The change in the momentum of the ball is:
A) zero
B) 0.5 N. s away from wall
C) 0.5 N . s toward wall
D) 3.5 N .s away from wall
E) 3.5 N .s toward wall
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large wedge with a mass of 10 kg rests on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown. A block with a mass of 5.0 kg starts from rest and slides down the inclined surface of the wedge, which is rough. At one instant the vertical component of the block's velocity is of 3.0 m/s and the horizontal component is 6.0 m/s. At that instant the velocity of the wedge is: 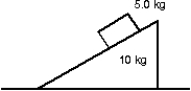
A) 3.0 m/s left
B) 3.0 m/s, right
C) 6.0 m/s, right
D) 6.0 m/s, left
E) 17 m/s, right
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 81
Related Exams